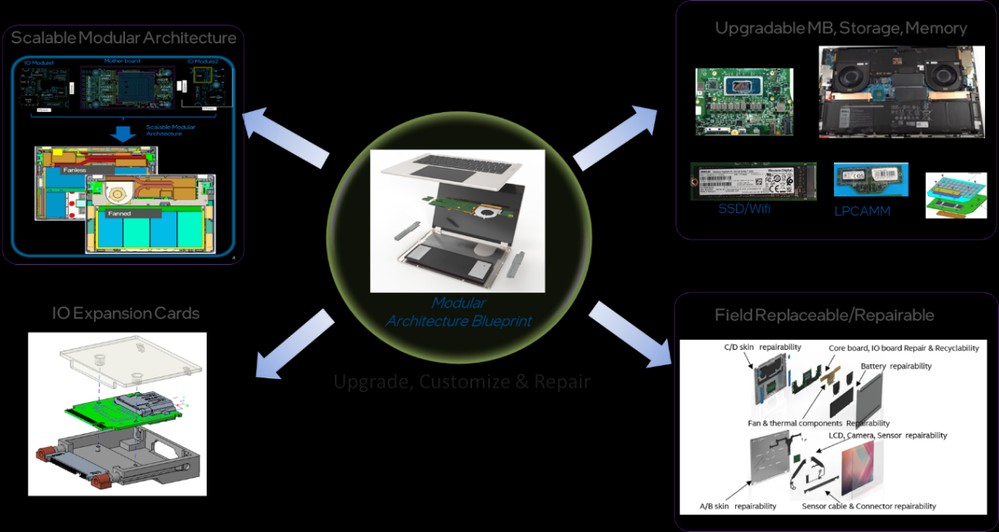
Intel has unveiled a new proposal for standardized modular laptop and mini PC designs that could revolutionize how users upgrade and repair their devices. The initiative aims to reduce electronic waste and cut costs by enabling component-level upgrades rather than complete device replacements.
The proposed standards would establish uniform measurements for laptop motherboards and I/O modules, allowing users to upgrade or replace individual components like USB-C ports, Thunderbolt connections, and mainboards without purchasing an entirely new machine.
For mainstream laptops, Intel's plan includes specifications for 14-inch and 16-inch devices with options for single or dual-fan cooling systems. The mini PC standards feature a 5L chassis design with slide rails for easy access to components like CPU, memory, GPU, and storage.
While companies like Framework and MNT already offer modular laptops, their solutions are limited to their own ecosystems. Intel's proposal could create an open marketplace similar to desktop PCs, where users can mix and match components from different manufacturers.
The standardization effort could also mark a win for the right-to-repair movement, which has been pushing back against manufacturers' restrictions on user repairs and third-party maintenance. Recent trends have seen many laptop makers limiting user-upgradeable components like RAM and SSDs.
However, the success of this initiative depends on industry-wide adoption. If manufacturers embrace these standards, it could lead to a more sustainable and user-friendly approach to laptop design, reducing both electronic waste and the total cost of ownership for consumers.
The proposal represents a potential shift away from the current model where aging laptops typically require complete replacement, as most only allow basic storage or memory upgrades. By enabling more comprehensive component upgrades, users could extend their devices' lifespan while keeping up with technological advances.