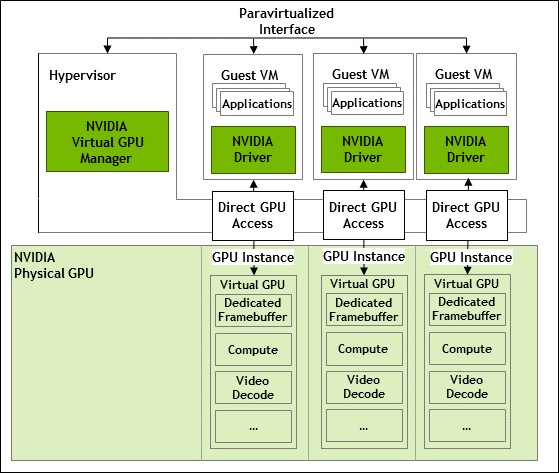
In a groundbreaking move, NVIDIA has released open-source Linux driver code to support GPU virtualization, also known as vGPU. This development marks a significant step forward in the realm of virtual machine (VM) technology and GPU utilization.
What is vGPU?
NVIDIA's vGPU technology allows a single physical GPU to be split into multiple virtual GPUs. These virtual GPUs can then be assigned to different VMs running concurrently. This capability is particularly valuable in enterprise environments where resource optimization is key.
The New Driver Code
The newly released code consists of 29 patches, currently labeled as a "request for comments." These patches aim to add vGPU support to the Nouveau NVKM driver code and introduce a "vgpu_mgr" as a VFIO virtual GPU manager specifically for NVIDIA GPUs.
This upstream-focused code is designed to work with NVIDIA Ada GPUs and newer models. It supports both Windows and Linux guest VMs, offering flexibility for various virtualization scenarios.
Implications for the Linux Community
This release represents a shift in NVIDIA's approach to open-source support. While the company has faced criticism in the past for not maintaining upstream, in-tree kernel graphics driver support, this move demonstrates a commitment to engaging with the open-source community.
The code is intended to be a full-fledged product for customer use, not just a proof of concept. It aims to provide simplified virtualization infrastructure on the host side, addressing a significant demand in the market.
Future Prospects
NVIDIA engineer Zhi Wang has provided a video demonstration of the code in action, showcasing its capabilities. The company plans to backport this technology to many older kernels, highlighting its potential for widespread adoption.
Industry experts suggest that this development could be a sign of things to come in the next decade. As the complexities and demands of HPC/AI servers continue to increase, and PCIe speeds rise, such innovations will be crucial for maintaining efficiency and performance.
This open-source release by NVIDIA not only enhances GPU virtualization capabilities but also strengthens the company's position as a contributor to the Linux kernel ecosystem. It opens up new possibilities for GPU utilization in virtualized environments and sets the stage for further advancements in this field.